🤔 What’s RAG?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are highly capable but encounter several issues like creating inaccurate or irrelevant content (hallucinations), using outdated information, and operating in ways that are not transparent (blackbox reasoning). Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique to solve these problems by augmenting LLM knowledge with additional domain specific data.
A key use of LLMs is in advanced question-answering (Q&A) chatbots. To create a chatbot that can understand and respond to queries about private or specific topics, it’s necessary to expand the knowledge of LLMs with the particular data needed. This is where the RAG can help.
🔧 Basic RAG Pipeline
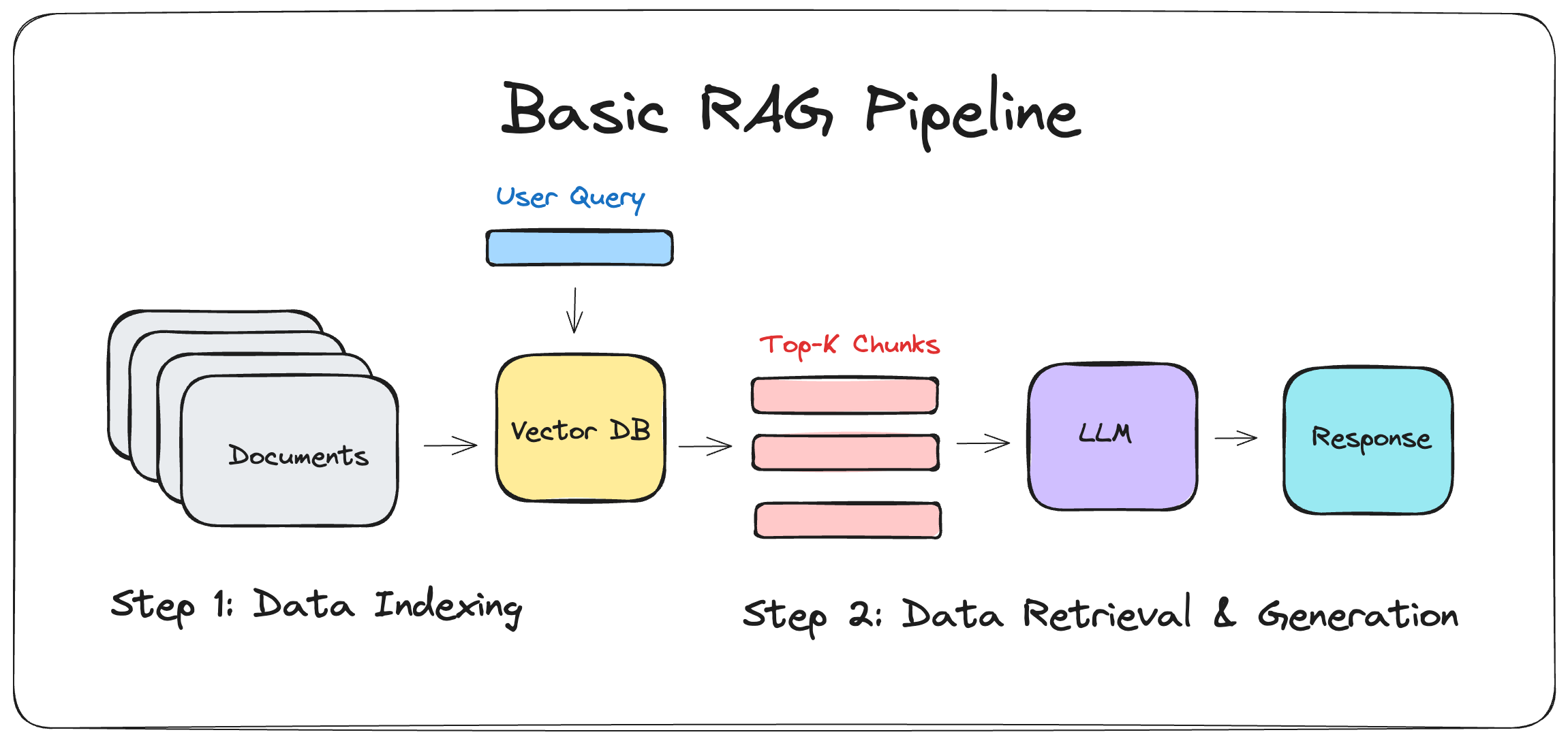
Here is how the Basic RAG Pipeline looks like:

Basic RAG Pipeline sketch by Julija | 📔 DrJulija’s Notebook | Follow my Medium Blog
The Basic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Pipeline operates through two main phases:
- Data Indexing
- Retrieval & Generation
Data Indexing
- Data Loading: This involves importing all the documents or information to be utilized.
- Data Splitting: Large documents are divided into smaller pieces, for instance, sections of no more than 500 characters each.
- Data Embedding: The data is converted into vector form using an embedding model, making it understandable for computers.
- Data Storing: These vector embeddings are saved in a vector database, allowing them to be easily searched.
Retrieval and Generation
- Retrieval: When a user asks a question:
- The user’s input is first transformed into a vector (query vector) using the same embedding model from the Data Indexing phase.
- This query vector is then matched against all vectors in the vector database to find the most similar ones (e.g., using the Euclidean distance metric) that might contain the answer to the user’s question. This step is about identifying relevant knowledge chunks.
- Generation: The LLM model takes the user’s question and the relevant information retrieved from the vector database to create a response. This process combines the question with the identified data to generate an answer.
🏗 How to Build a Basic RAG?
The most popular python libraries for building custom RAG applications are:
💡 You can create a Basic RAG Pipeline in a few lines of code!
Below code snippet creates a Basic RAG Pipeline for PDF document Q&A.
# import libraries
import os
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY') # add your OpenAI API Key
# for this example I used Alphabet Inc 10-K Report 2022
# https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1652044/000165204423000016/goog-20221231.htm
DOC_PATH = "../alphabet_10K_2022.pdf"
CHROMA_PATH = "your_db_name"
# ----- Data Indexing Process -----
# load your pdf doc
loader = PyPDFLoader(DOC_PATH)
pages = loader.load()
# split the doc into smaller chunks i.e. chunk_size=500
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50)
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(pages)
# get OpenAI Embedding model
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
# embed the chunks as vectors and load them into the database
db_chroma = Chroma.from_documents(chunks, embeddings, persist_directory=CHROMA_PATH)
# ----- Retrieval and Generation Process -----
# this is an example of a user question (query)
query = 'what are the top risks mentioned in the document?'
# retrieve context - top 5 most relevant (closests) chunks to the query vector
# (by default Langchain is using cosine distance metric)
docs_chroma = db_chroma.similarity_search_with_score(query, k=5)
# generate an answer based on given user query and retrieved context information
context_text = "\n\n".join([doc.page_content for doc, _score in docs_chroma])
# you can use a prompt template
PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """
Answer the question based only on the following context:
{context}
Answer the question based on the above context: {question}.
Provide a detailed answer.
Don’t justify your answers.
Don’t give information not mentioned in the CONTEXT INFORMATION.
Do not say "according to the context" or "mentioned in the context" or similar.
"""
# load retrieved context and user query in the prompt template
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(PROMPT_TEMPLATE)
prompt = prompt_template.format(context=context_text, question=query)
# call LLM model to generate the answer based on the given context and query
model = ChatOpenAI()
response_text = model.predict(prompt)
print(response_text)
"""
Generated response:
The top risks mentioned in the provided context are:
1. Decline in the value of investments
2. Lack of adoption of products and services
3. Interference or interruption from various factors such as modifications, terrorist attacks, natural disasters, etc.
4. Compromised trade secrets and legal and financial risks
5. Reputational, financial, and regulatory exposure
6. Abuse of platforms and misuse of user data
7. Errors or vulnerabilities leading to service interruptions or failure
8. Risks associated with international operations.
"""